Why Zinc?
Ever wonder why zinc (Zn) is used for corrosion protection on Ductile iron pipe (DI pipe)? Or how thick the zinc coating is and how it is applied? Today we will answer those questions and cover when a zinc coating might be recommended.
Among non-ferrous anodic metals to assist with corrosion protection, zinc is one of the most readily available and least expensive. Additionally, all zinc-coated pipe is supplied with a topcoat, so it is also NSF 61 approved for potable water service. Its lightweight, self-healing nature can provide supplemental corrosion protection that synergizes well with the primary corrosion protection of V-Bio® Enhanced Polyethylene Encasement. For more information on when and where to employ a zinc coating, please see this Iron Strong Blog by my former colleague Brian Richard on Why Zinc on Ductile Iron Pipe and What's The Hype?
Brief History of Zinc Coatings
Zinc coatings were first introduced in Europe beginning in the mid 1950's. In 1985, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) created the first application standard for zinc-coated Ductile iron pipe with the publication of ISO 8179-1, Ductile iron pipes, fittings, accessories and their joints - External zinc based coating, Part 1: Metallic zinc with finishing layer.
Ductile iron manufacturers in North America began applying zinc at around this same time for pipe intended for export. In the United States (U.S.), polyethylene encasement was the most common and cost-effective method used for corrosion control.
Around 2015, zinc-coated pipe began to be promoted in the U.S. as well. Although the original ISO standard for zinc application has been updated several times, the current requirement is 200 g/m2 (or approx. 1 mil) w/bitumen topcoat as a minimum. Therefore, domestic DI pipe with zinc coating is supplied with this same amount. It is also recommended that to achieve optimal performance, zinc-coated pipe also be installed with polyethylene encasement, too.
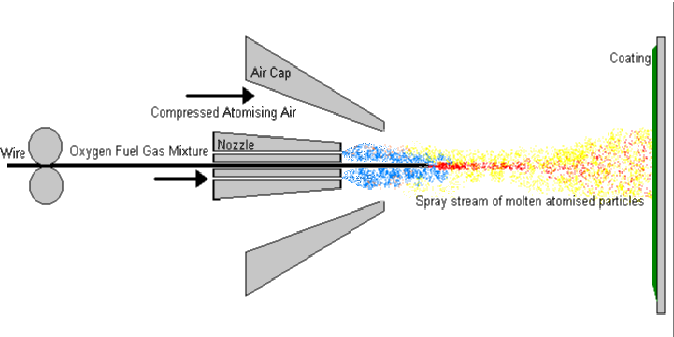
How Zinc Coating is Applied
High purity zinc wire is atomized into metallic droplets via an arc spray process using clean compressed air to propel the zinc to the pipe's surface as the pipe rotates. The pipe rotation speed and air pressure employed are carefully controlled, providing a uniform application of 200 g/m2. While surface prep is not a particular concern with this type of zinc application, the minimization of moisture on the surface to be coated is critical to the quality of the coat, as this is after all, an electric-arc driven process.
How Zinc Helps to Protect Ductile Iron Pipe
Zinc bonds exceptionally well to the annealing oxide layer on Ductile iron pipe, which already adds to the inherent corrosion resistance of DI pipe. Zinc is anodic to iron and will protect the pipe in a manner akin to cathodic protection. In doing so, a zinc oxide and other protective compounds are byproducts that also serve to protect the pipe. The bituminous asphalt topcoat (1-2 mils) can assist with isolating the zinc from the soil, enhancing its ability to protect the pipe.
Common Questions about Zinc Coating
- Can wedge action restraint glands, similar to TUF Grips™, be used on zinc- coated pipe? Yes
- Can zinc-coated pipe be used with locking type gaskets such as Sure Stop 350®? Yes
- Can zinc-coated pipe be cut in the field? Yes, zinc application is compatible with standard push-on or mechanical joints, which allows field cuts in the same way as non-zinc coated pipe. Additional PPE, respiratory protection, may be required when cutting zinc-coated pipe.
- Can cathodic protection be added on zinc-coated pipe? Yes, cathodic protection systems may be added to any new installation. Decisions to implement any type of cathodic protection should be based on the Consequence and Likelihood results from The Design Decision Model®.
- How much life expectancy does zinc add to the pipe? Zinc is a betterment to the use of V-Bio enhanced polyethylene encasement that will add service life to your DI pipe. The amount of extended life will be site-specific and depend on several factors, including soil characteristics, the quality of the encasement installation, etc.
- Which pipe manufacturers can supply zinc coating? All domestic DI pipe manufacturers can supply zinc-coated pipe.
- How do we identify DI pipe that has a zinc coating? McWane Ductile will apply blue paint to the bell face of any zinc-coated pipe. Additionally, "ZINC" will be displayed on the cast sticker located at the bell end of each pipe. For more great information on Ductile Iron Pipe Markings: What Do They Mean? see this Iron Strong Blog from my colleague Jeff Houser
Can Zinc-Coated Pipe be Installed Without V-Bio®?
McWane Ductile does not recommend that zinc-coated pipe be installed without V-Bio enhanced polyethylene encasement. Zinc is not considered standalone corrosion protection system, and therefore we only recommend its application and use when field investigation and test results support such a decision.
V-Bio provides active corrosion prevention and is non-consumptive. The zinc coating would provide secondary protection, where needed, when damage to the encasement may have occurred. We endorse using the recently updated Design Decision Model® (DDM®) as a guideline for recommended corrosion protection levels.
Key Takeaways:
After reading this article, I hope that you take away a few key points:
- Measures taken to mitigate corrosion concerns for a water or wastewater pipeline by providing additional coating systems should be based on the results of a corrosion study and the resulting consequence should any potential corrosion occur.
- Applying zinc with a topcoat to Ductile iron pipe has the potential to benefit its service life. However, it is recommended that the pipe also be installed with V-Bio enhanced polyethylene for this benefit to be fully realized. Zinc is not recommended as a standalone corrosion control system.
- V-Bio® enhanced polyethylene encasement with metalized zinc coating is recommended only for zones 4 and 5 of The Design Decision Model®.
Need Assistance with Your Waterworks Project?
Please contact McWane Ductile and one of our NACE Certified Corrosion Technicians. They would be happy to assist with evaluating your job site conditions to ensure that you specify the appropriate method of corrosion protection for your project.
We have team members who have managed small and large water utility systems, served in engineering consulting firms, and bring decades of experience in solving field issues involving pipeline construction and operation. From design to submittal, to installation, we strive to provide education and assistance to water professionals throughout the water and wastewater industry.
Check Out All Our Digital Offerings
Sources
- Paris, M., “Zinc Based Coating for Protecting Buried Gray and Ductile Iron Pipes Against Corrosive Soils,” Pont-a-Mousson, France, Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Internal and External Protection of Pipes, University of Durham, Durham, England, September 9-11, 1975
- ISO 8179-2:2017 Ductile iron pipes, fittings, accessories, and their joints — External zinc-based coating
- Corrosion Protection for Ductile Iron Pipe, David Kroon, et al, Corrpro Companies Inc., Materials Performance (NACE) 2005
- Marchal, R., “Protection of Buried Ductile Iron Pipelines with a Zinc Based Coating – Healing Power of Coating Damages,” Pont-a-Mousson Research Center, Pont-a-Mousson, France, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on the Internal and External Protection of Pipes, Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, September 15-17, 1981
- Pipelines 2020 - A 60‐year History of the Efficacy of Polyethylene Encasement of an Iron Pipe Installation in an Aggressive Soil Environment L. G. Horn, P.E., M. ASCE, VP – Technical Resources, DIPRA