The choice of materials in water infrastructure is crucial in ensuring the system's durability and reliability and influencing operational costs. Water and wastewater treatment plants are typically the largest energy consumers for municipalities, accounting for 30 to 40% of total energy consumption. To protect their systems from overload, energy companies must implement rolling blackouts during extreme weather.

What is a Rolling Blackout?
A rolling blackout is a controlled, temporary power outage that prevents the electrical power grid from overloading. During a rolling blackout, electricity is shut off to different parts of a distribution region for non-overlapping periods. Rolling blackouts are a last-resort measure electric utility companies use to avoid a total blackout. They can be caused by several factors, including:
- Weather conditions that damage power lines
- Increased demand for power, such as during a heat wave or cold snap
- An overloaded power grid
Municipalities should focus on reducing their energy consumption to ensure lower water and sewer bills for customers and to help decrease the energy demand on the nation’s energy grid. Reducing the electrical demand from municipalities across the county could help prevent rolling blackouts and provide a more reliable energy grid. This #IronStrong Blog discusses the benefits of using Ductile iron pipe (DI pipe) in your utility water system and how its key advantages can save you money compared to other materials.
How does the design advantage of Ductile iron pipe save money?
Lower Pumping Costs
All too often, utilities are unaware of the potentially significant energy savings over the life cycle of the pipe material. Many do not make the proper flow rate comparisons and instead focus solely on the price per foot on the bid form. They ultimately pay more in the long run. Ductile iron pipes have a smooth internal surface, which minimizes frictional losses during water flow, similar to the smoothness of other internal pipe surfaces, such as PVC and HDPE. The reduced friction means less energy is required to pump water through the system. As a result, water utilities can achieve notable energy savings, translating into lower electricity bills over time.
Optimal Flow Characteristics
The design of Ductile iron pipe allows for optimal flow characteristics. Their consistent and smooth interior prevents turbulence, ensuring a steady and efficient water flow. This inherent efficiency in water transport can lead to decreased energy consumption compared to systems with less optimized pipes. Regarding the INSIDE DIAMETER of water pipelines, bigger is better when a utility looks at the monthly electric bills for pumping water throughout the system. Why is this the case?
Four factors that affect water resistance through a pipeline
When water flows through a pipeline, four factors affect the resistance to that flow:
- The INTERNAL DIAMETER of the pipe
- The velocity of the water flow
- The roughness of the interior surface of the pipe and
- The length of the pipeline.
When all these variables are identified, they can be placed into the well-known Hazen-Williams Formula to determine the head loss occurring in the pipeline. Because the value of the inside diameter appears in the denominator of the Hazen-Williams formula, the larger the inside diameter, the smaller the head loss. Due to its larger inside diameter, Ductile iron outperforms other competing pipe materials in terms of pipeline flow rates.

So, what is the practical side of this evaluation for the water utility?
To get water to customers at adequate pressure, head losses must be overcome using pumps to apply energy. Head loss is the reduction in the fluid's total head (pressure) as it moves through a pipeline. This energy costs the water utility in the form of an electric bill. The less power that must be applied, the lower the utility's electric bill and the utility's customers' water and sewer rates.
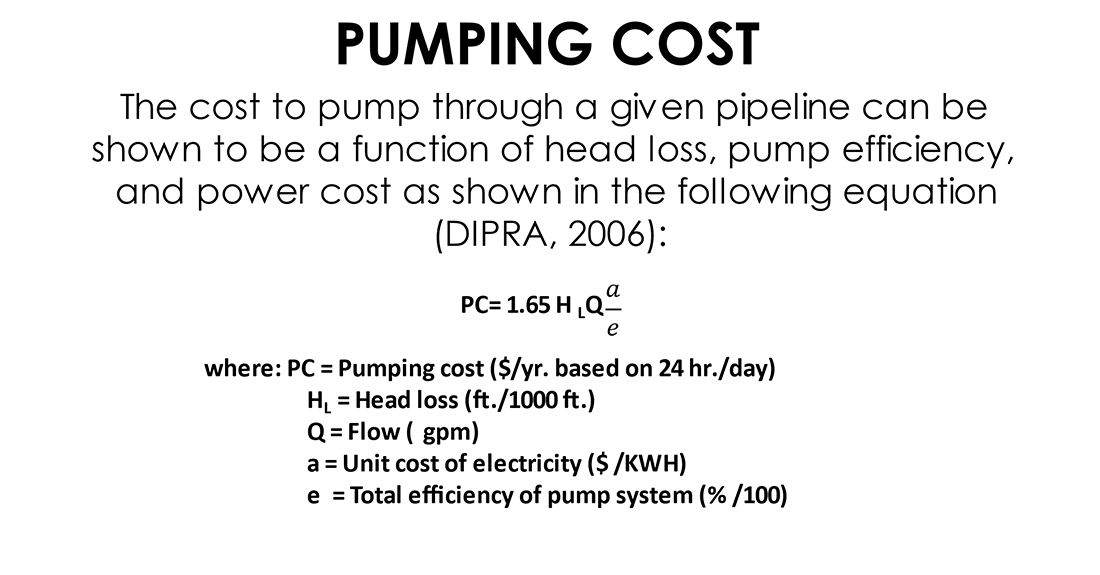
These annual cost savings can be easily calculated using the head loss value and inserting that value into a pumping cost equation such as that used in the University of Michigan Study “A Framework to Evaluate the Life Cycle Costs and Environmental Impacts of Water Pipelines” (ASCE Conference Proceedings, Pipelines 2016). They can even be further extended by evaluating pumping cost savings over many years using a present-worth approach. This long-term cost-effectiveness of DI pipe can make water utilities feel financially prudent and responsible.
These calculations can be conveniently performed using the Energy Savings Calculator on the McWane Pocket Engineer mobile and desktop app. The calculator evaluates the inside diameters of different pipeline materials against that of Ductile Iron, allowing the user to be confident in their decision-making process.

Head Loss Equates to Money Loss
I mentioned earlier that the roughness of the pipe's interior surface is a factor in calculating head loss. This is commonly known as the pipe's “C” factor. It should be noted that although some other pipe materials have higher “C” factors due to the presence of smoother inside surfaces, this component doesn’t affect pipeline flows nearly as much as increased inside diameter. Research has also found that the “C” factor of Ductile iron pipe remains consistent throughout many years of service.
Now, let’s look at an example of a utility installing a mile-long 8” pipeline in a subdivision. The materials being evaluated and considered are Ductile iron pipe and PVC.
In determining the energy costs to the utility of each respective material, the project model, as noted in the information below, has been established (Please note that these rates apply to the time of the publication):
- 8” DI Pipe vs. 8” PVC Pipe
- Pipeline Length: 5,280 ft.
- C Factor: 140
- Flow Rate: 695 GPM (Tech Park Demand)
- Unit Power Cost: 0.06 $/kWh
- Pump Rate: 24 hr/day
- Pump Efficiency: 70%
- Design Life: 100 Years
- Rate of Return: 5%
- Inflation Rate: 4%
By going through the steps of first determining the respective head loss that must be overcome in each pipeline, then converting that into pumping costs the utility will incur based on the assumptions listed, one finds that using Ductile iron pipe will result in a cost savings to the utility of over $80,000 during the 100-year estimated service life of the ductile iron pipe. The reason for this cost savings to the utility is that the 8” DI pipe (Class 350) has a 9.76% larger inside diameter than the 8” PVC pipe (DR-14).
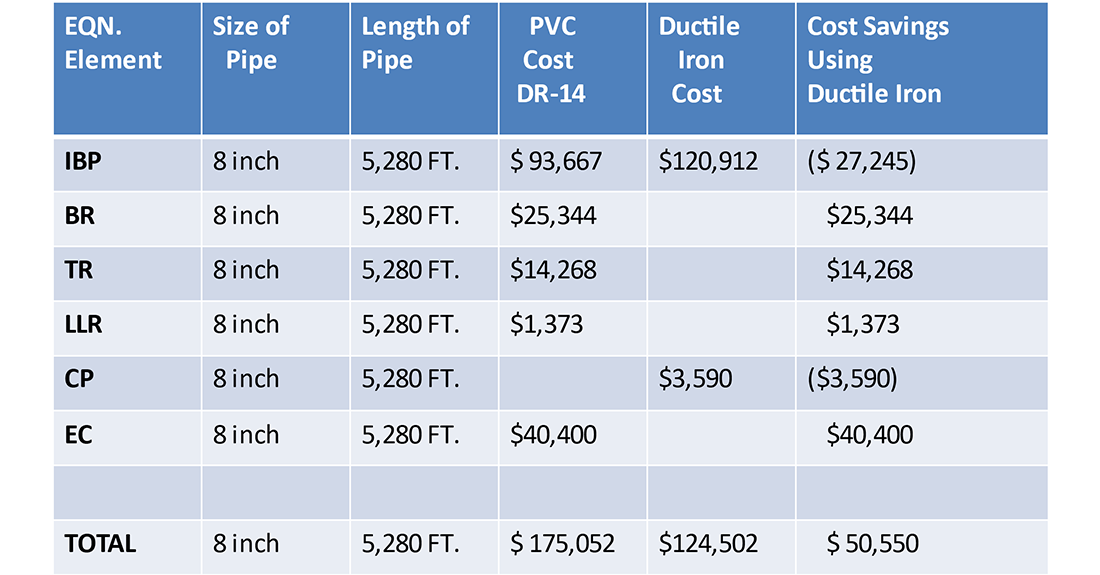
Calculating savings with Ductile iron pipe
Water utility companies can enhance their cost savings by considering larger pipelines, which typically carry more significant flows through the system.
|
Length of pipe: |
30,000 ft. |
|
Flow rates: |
6,000 gpm |
|
Unit power cost: |
$0.10/kwh |
|
Pump efficiency: |
70% |
|
Pump rate: |
24hr/day |
|
Design life: |
100 years |
|
Rate of return: |
5% |
|
Inflation rate of power cost: |
3% |
Using the same approach in calculating the cost savings using the present worth analysis commonly used by engineers and planners of the utility when considering a 24” pipeline under the assumptions above, you find that respectively:
- DI Pipe will result in a $1,213,307 present worth of savings over PVC pipe.
- DI Pipe will result in a $672,178 present worth of savings over Steel and Concrete pipe.
- DI Pipe will result in a $3,208,741 present worth of savings over HDPE.
How does the durability advantage of Ductile iron pipe save money?
DI pipe has up to 13 times more strength than plastic pipe
Impact strength is an essential characteristic of piping materials. While this property relates more to conditions the pipe might encounter during handling, shipping, and installation, it is crucial because damage incurred during these activities can go undetected and later result in failures in the operating pipeline.
Reduced Maintenance Downtime
Ductile iron pipes are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Their extended lifespan means less frequent maintenance and replacement, reducing water system downtime. A system that operates smoothly and requires fewer repairs contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings in the long run.

What is the sustainability advantage of Ductile iron pipe?
Environmentally Friendly
Ductile iron pipe is made from up to 95% recycled scrap iron and steel. DI pipe can also be recycled, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Choosing sustainable materials aligns with modern practices of reducing carbon footprints. As utilities and municipalities strive to adopt eco-friendly solutions, using DI pipe can be a step toward sustainability and responsible resource management.
McWane Ductile facilities are among the manufacturing leaders in their regions, using recycled materials for their water pipe and electric utility pole products. Additionally, they have implemented environmental practices that, in many instances, exceed national standards. Supporting these efforts is a robust environmental management system that helps assure compliance with applicable environmental regulations, standards, permit conditions, and voluntary commitments.
Plastic pipe is derived from toxins
PVC pipe is made from chlorine (derived from salt) and carbon (predominantly derived from oil and gas via ethylene). PVC is also derived from vinyl chloride, which is a toxin. It is made rigid by adding a stabilizer, and at one time, the PVC industry used lead as a stabilizer. Today, PVC manufacturers use other chemicals that may pose health risks, but some foreign manufacturers continue to use lead. In addition, the recycled content of PVC is nearly zero, and PVC can only be downcycled.
HDPE pipe is made from ethylene derived from oil and natural gas. To form an HDPE pipe, ethylene in pellet form is melted into a molding machine and then extruded into its finished pipe form. Little, if any, true recycling is involved with HDPE products manufactured for the water and sewer industry.
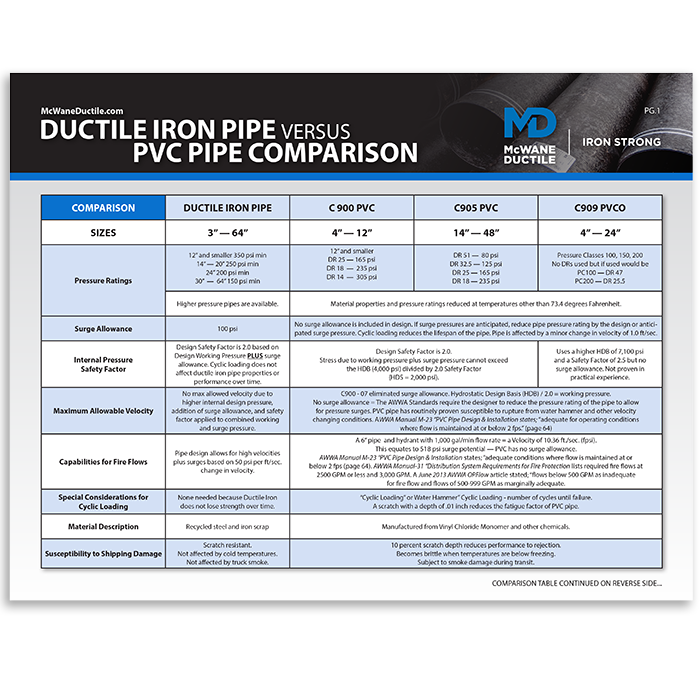
What are the differences and advantages of Ductile iron over PVC pipe? Many things! Use this handy comparison sheet to ensure you specify the safest, durable, and longest-lasting pipe for your next project.
DOWNLOAD NOW
In conclusion – Ductile iron pipe saves energy and money
After reading this Iron Strong blog, you can see why Ductile iron pipe is a favored solution for water distribution systems. It offers various benefits over alternate materials. Energy savings are important to utilities and their end-consumers and should always be . As water utilities and municipalities explore ways to reduce energy consumption, cut operational costs, and embrace sustainable practices, adopting DI pipe emerges as a wise, practical, and forward-thinking decision.
The reduced pumping costs, optimal flow characteristics, minimal maintenance requirements, and environmental sustainability make DI pipe an attractive choice for those looking to make their water systems more durable and energy-efficient. In the long run, choosing DI can translate into tangible savings on your electric bill, reducing electrical demand on the nation’s energy grid and contributing to a more resilient and sustainable water infrastructure. Most of the utility’s capital investment is underground. When planning for investment in the critical components of your system, ALL factors should be considered.
Need Assistance with Your Waterworks Project?
If you have any questions regarding your water or wastewater infrastructure project, your local McWane Ductile representative is equipped with the expertise to assist you. Many of our team members have managed small and large water utility systems, served in engineering consulting firms, and bring decades of experience solving field issues involving pipeline construction and operation. From design to submittal to installation, we strive to educate and assist water professionals throughout the water and wastewater industry.







